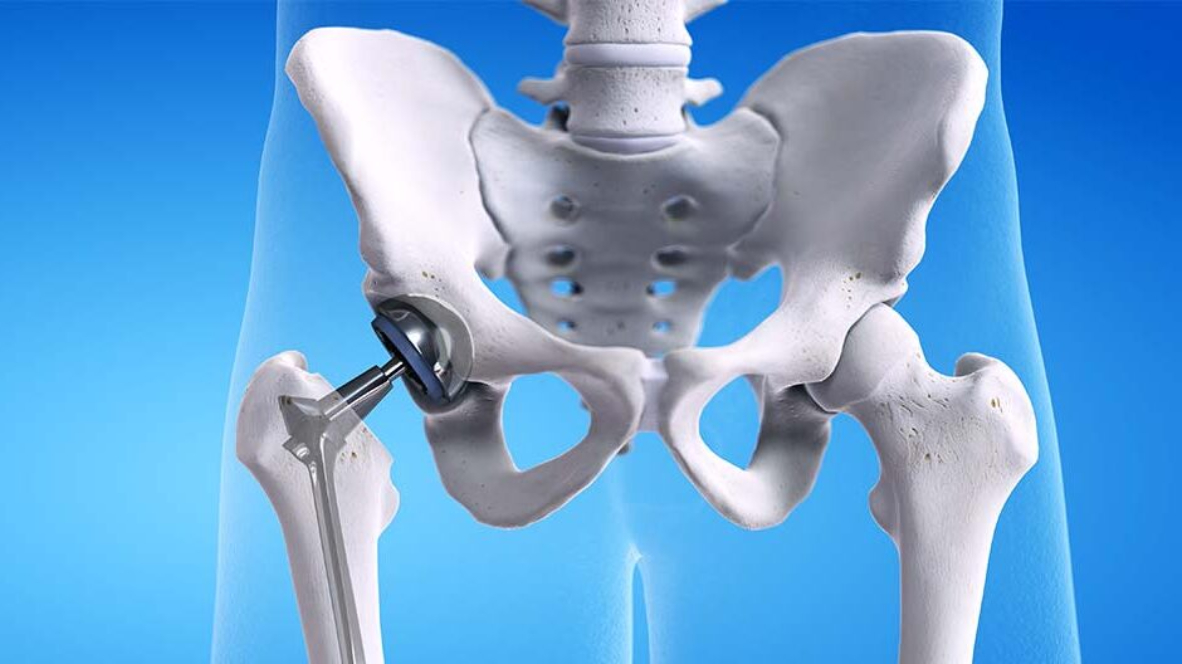
Patients guide to Total Hip Replacement
Total Hip Replacement is a surgery in which diseased and destroyed joint i.e ball (head of femur) is removed and replaced with a ceramic or metal ball and metal stem, the acetabulum ,socket (cup) is relined with a poly or metal cup.
ANATOMY
Hip joint is a ball and socket type of diarthrodial joint .
Head of femur (thigh bone) articulates with acetabulum (cup ) to form hip joint surrounded by capsule and ligaments i.e iliofemoral ligament, ishiofemoral ligament, pubofemoral ligament, legamentum teres, transverse acetabular ligament.
Femoral head with anteversion 15 degrees and neck shaft angle of avg 135 degrees in an adult.
Conditions Which Cause Hip Pain and Invariably Result in Incongruency of the Hip Joint
Osteoarthritis. This is an age-related “wear and tear” of the joint cartilage and the underlying bone.
Rheumatoid arthritis. This is an autoimmune disease in which the synovial membrane becomes inflamed and thickened
Post-traumatic arthritis. This can follow a serious hip injury or fracture. The cartilage may become damaged and lead to hip pain and stiffness over time.
Osteonecrosis. An injury to the hip, such as a dislocation or fracture, may limit the blood supply to the femoral head. This is called osteonecrosis, also referred as “avascular necrosis”. The lack of blood may cause the surface of the bone to collapse, resulting in arthritis
Childhood hip disease. Some infants and children have hip problems. Even though the problems are successfully treated during childhood, they may still cause arthritis later on in life. This happens because the hip may not grow normally, and the joint surfaces are affected.
Clinical Indication
Incapacitating pain of the hip joint
Limitation of hip movement
LLD Limb length discrepancy – unequal lower limb length
Walking with a limp
Clinical Examination
Inspecting the gait, how the patient walks in the room . routinely patient develops an antalgic gait or trendelenberg gait.
Palpating and eliciting tenderness over the hip joint line.
Examining the range of movement of hip by flexion, extension, adduction, abduction, internal and external rotation. All movements become painful and restricted.
SPECIAL TESTS
Fadir Test is positive if it produces pain when hip is flexed in 90 degree with adduction and internal rotation
Faber Test is positive if it produces pain when hip is flexed in 90 degree with abduction and external rotation. Positive FABER indicates intraarticular hip lesion.
Thomas Test to rule out Fixed flexion deformity.
Radiological Evaluation
X ray of pelvis with both hips in AP view is obtained.
Bilateral lower limb xray in AP view to examine alignment radiologically.
Pre Operative Evaluation
Routine Blood Investigations to Rule Out Any Infection
Management of Other Comorbidities
Fitness for Surgery by Physician and Anesthetist.
Surgery – Total Hip Arthroplasty
- The damaged femoral head is removed and replaced with a metal stem that is placed into the hollow center of the femur. The femoral stem may be either cemented or “press fit” into the bone.
- A metal or ceramic ball is placed on the upper part of the stem. This ball replaces the damaged femoral head that was removed.
- The damaged cartilage surface of the socket (acetabulum) is removed and replaced with a metal socket. Screws or cement are sometimes used to hold the socket in place.
- A plastic, ceramic, or metal spacer is inserted between the new ball and the socket to allow for a smooth gliding surface.
Post Operative Rehabilitation
0-3 WEEKS PHASE 1
Hip in Abduction for 6 Weeks to Avoid Prosthesis Dislocation
Gait Training and Mobilization with Walker
Static Quads, Static Hams , Knee Rom, Slr in Supine Plane, Ankle Pumps
Adl – Activities of Daily Life
3-6 WEEKS PHASE 2
Phase 1 Exercises and Isometric Strengthening of Hip
6-9 WEEKS PHASE 3
Phase 1,2 Exercises and Dynamic Strenthening of Hip
Clampshell Exercise in Short Arc
9-12 WEEKS PHASE 4
All Above Exercises
